 Physics
Physics Double-Slit Experiment and Schrödinger Equation
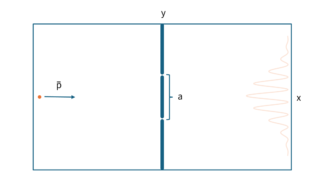
This article derives a solution to the Schrödinger equation for the double-slit experiment, and present the hypothesis that phenomena such as the double-slit experiment are caused by the properties of relativistic space-time.